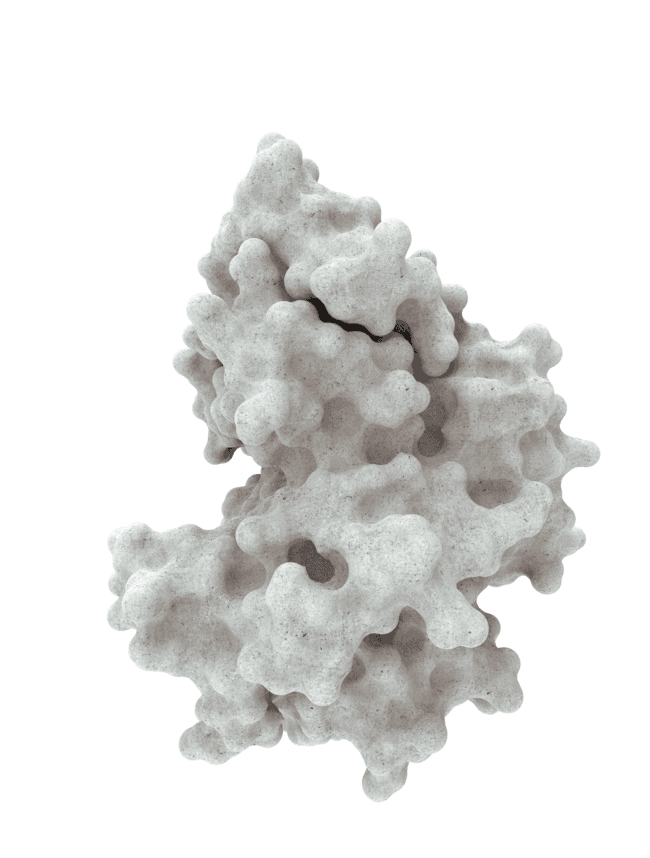
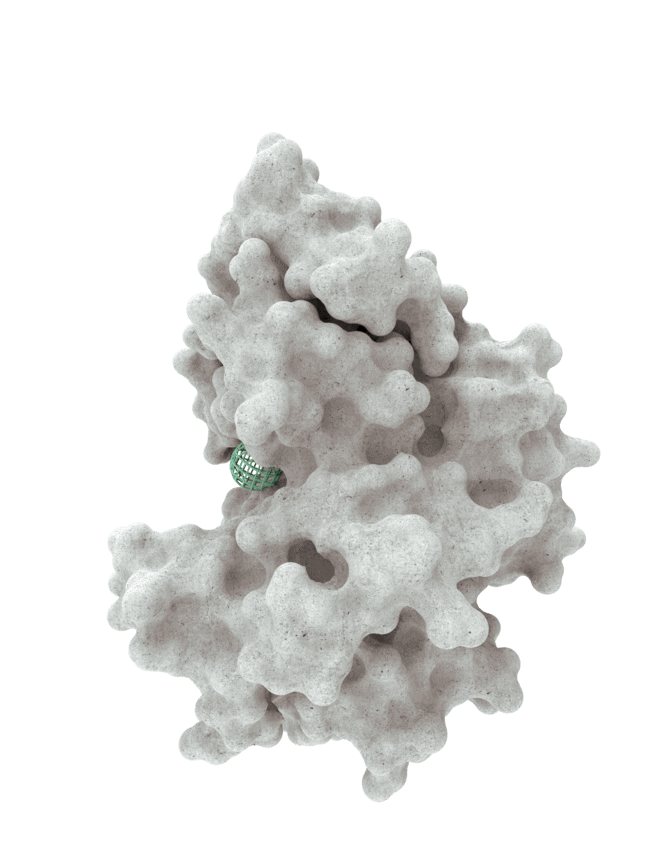
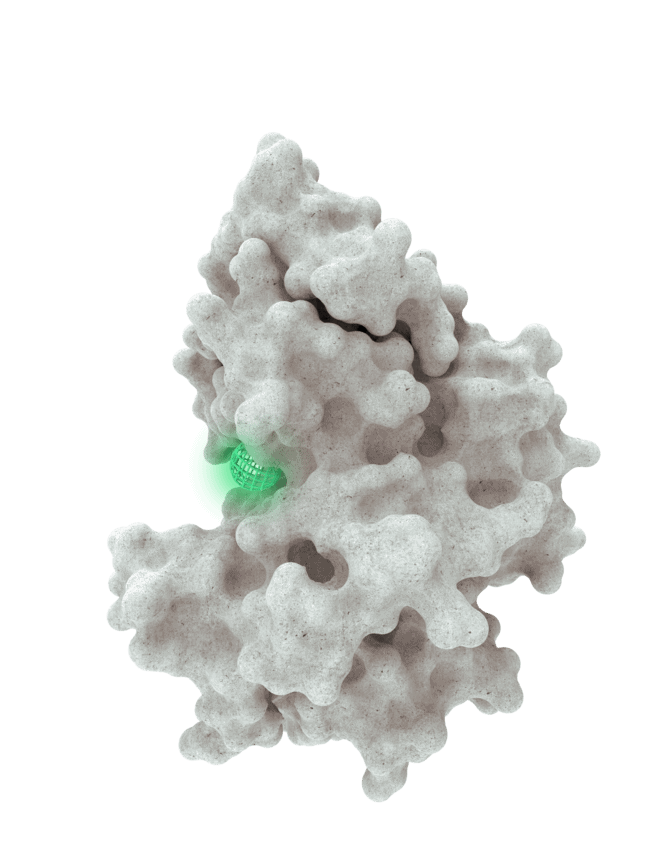
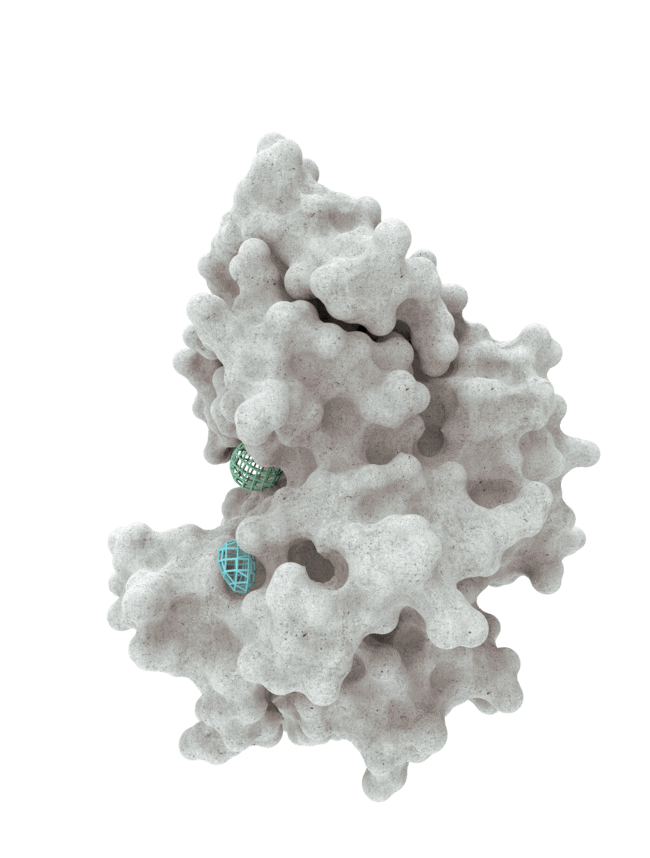
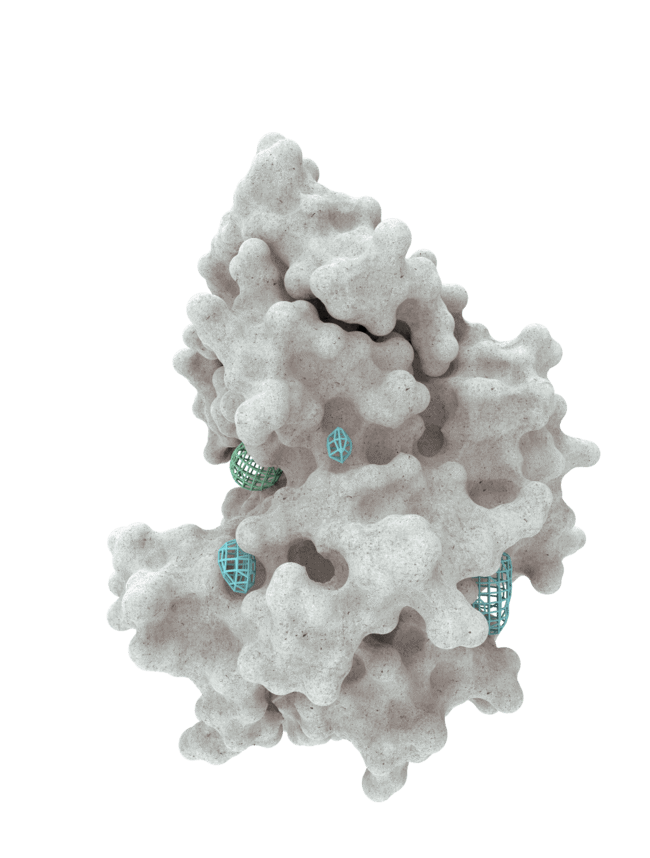
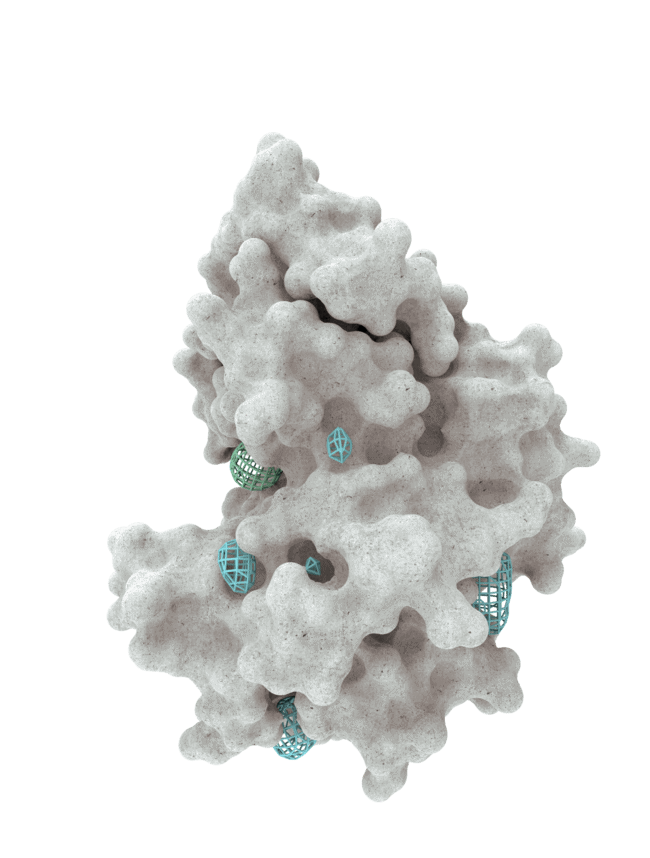
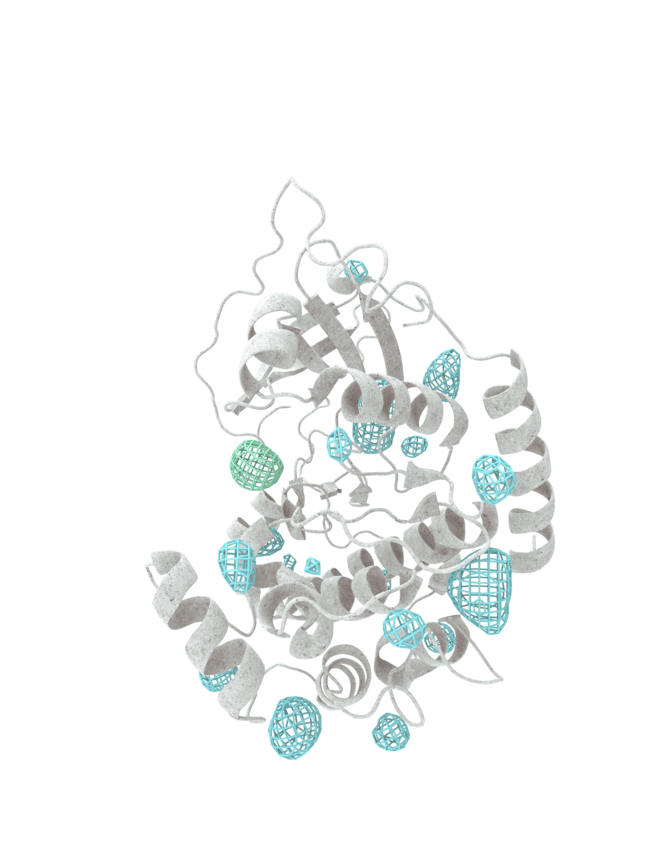
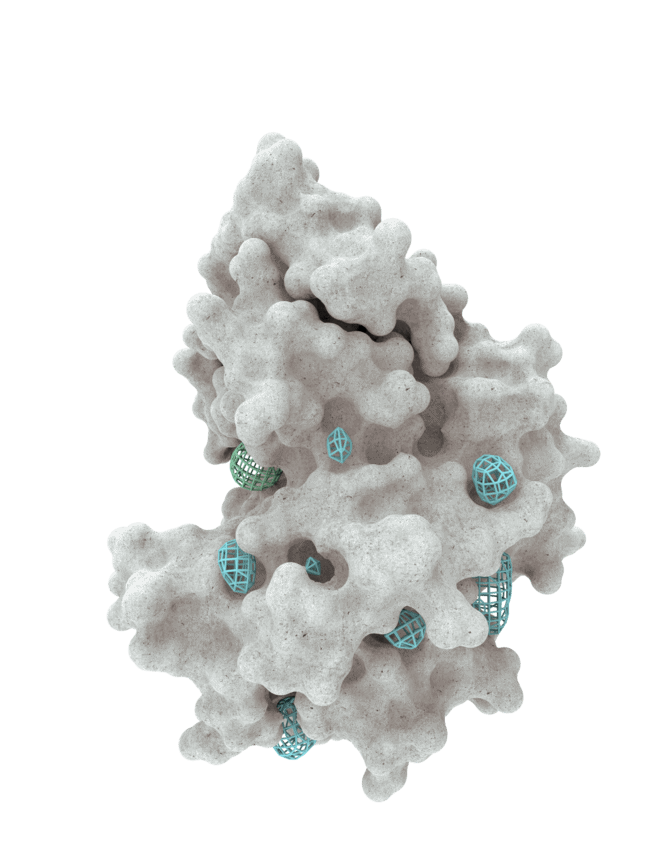
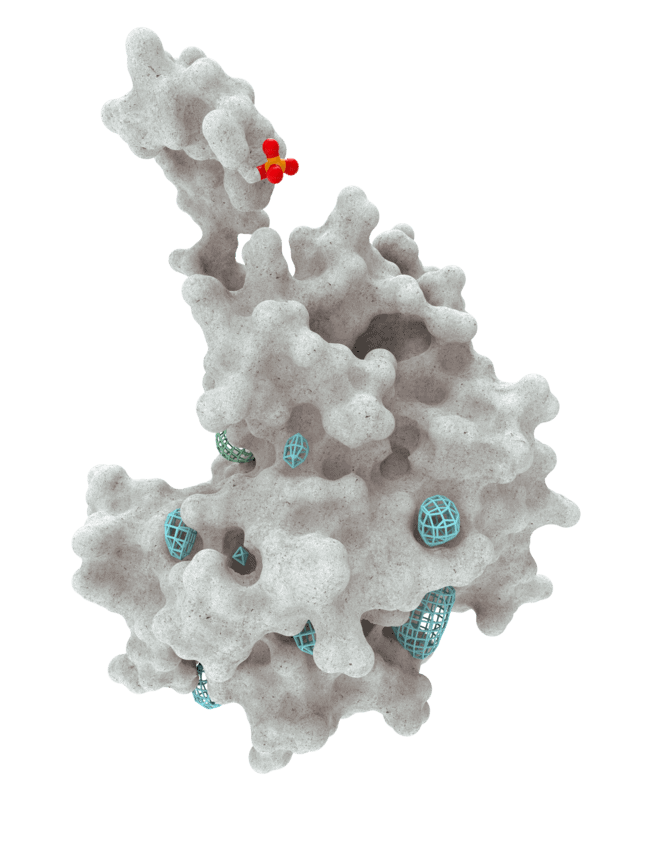
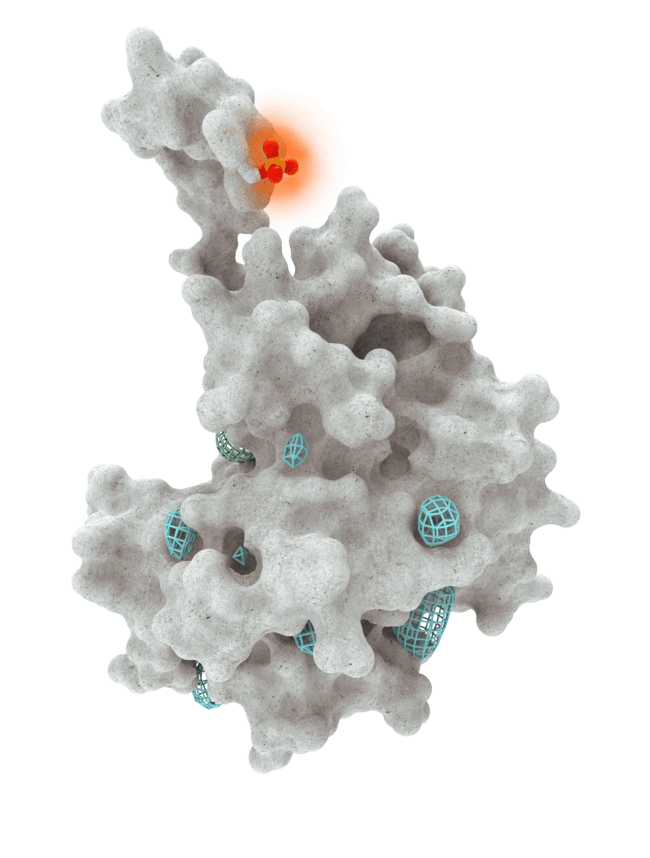
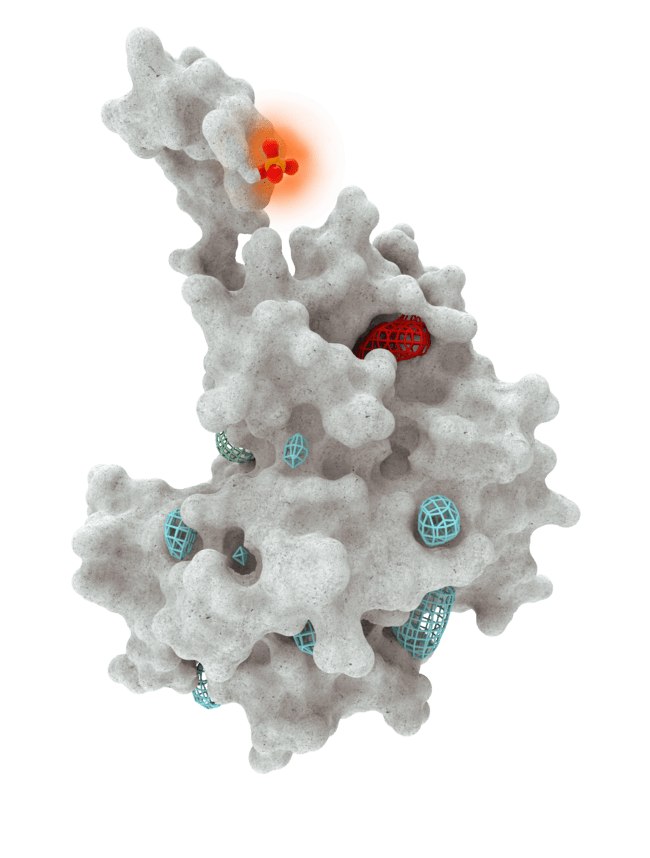
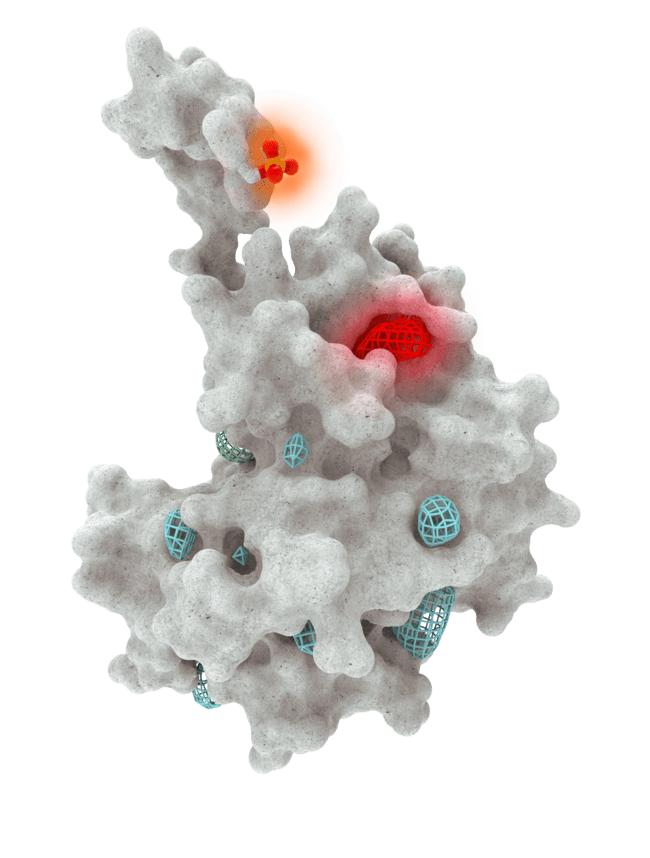
At HotSpot, we have moved beyond active site inhibition to create a groundbreaking new approach to drug discovery. By targeting allosteric protein pockets that drive function, we believe we can reprogram control mechanisms to deliver differentiated medicines.
Allosteric pockets may exist on most proteins and are not limited to those with substrate turnover sites only, enabling the targeting of previously inaccessible biological pathways relevant to serious diseases.
Allosteric therapeutics can modulate functions such as protein conformation, scaffolding and cellular translocation, resulting in broader, tunable pharmacology including protein inhibition, activation, degradation or stabilization.
The structures of allosteric pockets tend to differ significantly within a specific protein class, enhancing the ability to design drugs with a high degree of selectivity and minimizing the potential for off-target liabilities.
The balanced topography of allosteric pockets may simplify the engineering of drugs targeting these allosteric sites, leading to characteristics that facilitate improved patient convenience, such as reduced pill burden and dosing frequency.
Through natural hotspots, evolution has devised a means to selectively correct for chemical imbalances and dysregulation to restore health and proper functioning, both in normal biological activity and in disease.